The tundra is one of the most extreme and unique ecosystems on Earth. It is a biome characterized by cold temperatures, short growing seasons, and permafrost, where only a limited number of species can survive. However, even in these harsh conditions, life thrives. The role of producers in this environment is vital, and understanding “What’s a Producer in Tundra” is key to appreciating the balance of this fragile ecosystem.
In this article, we will explore 10 fascinating facts about the producers in the tundra and their essential role in maintaining the delicate balance of life in this environment.
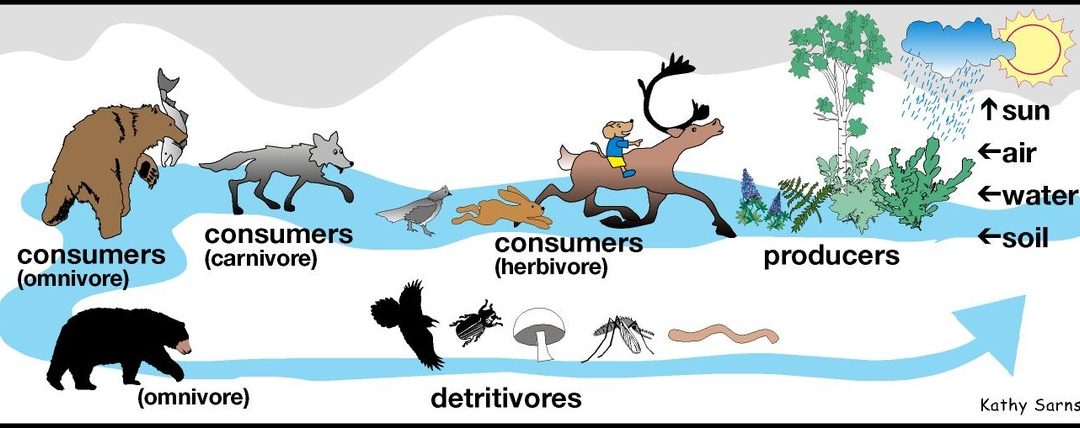
What’s a Producer in Tundra?
Before diving into the facts, it’s essential to understand the basic concept of a “producer” in the context of an ecosystem. In any biome, producers are organisms that can produce their own food through photosynthesis. These organisms, such as plants, algae, and some bacteria, form the base of the food chain by converting sunlight into energy. In the tundra, where the growing season is short and the climate is harsh, the producers are highly adapted to the extreme conditions. These adaptations allow them to thrive where other organisms cannot.
What’s a Producer in Tundra: Producers in Tundra Are Mostly Plants
In the tundra, the majority of producers are plants. However, these plants are often much smaller and more resilient than those found in more temperate regions. Mosses, lichens, and small shrubs dominate the landscape. These plants are adapted to the short growing season and cold temperatures of the tundra. Their ability to perform photosynthesis in such harsh conditions makes them the foundation of the tundra food web.
What’s a Producer in Tundra: Permafrost Limits Plant Growth
Permafrost is a defining feature of the tundra biome. This layer of permanently frozen soil makes it challenging for many plants to grow deep roots. The shallow soil and short growing seasons limit the size of plants, but certain species have adapted to these conditions. Many tundra producers, like mosses and lichens, have developed unique mechanisms to survive in these extreme environments. They grow in tight clusters that trap heat from the sun, and they have evolved to withstand the cold and dry conditions.
What’s a Producer in Tundra: The Role of Lichens in the Tundra
Lichens are a unique group of organisms that combine fungi and algae or cyanobacteria in a symbiotic relationship. In the tundra, lichens are one of the most important producers. They are able to survive in the harsh conditions by absorbing moisture from the air and forming resilient partnerships with other organisms. Lichens can survive freezing temperatures and provide vital food sources for herbivores, such as caribou, that depend on them during the winter months when other food is scarce.
Mosses: Tiny but Mighty Producers
Mosses are another key producer in the tundra, often forming thick mats that cover the ground. These plants are incredibly resilient and can survive extreme cold, low light, and a lack of nutrients. Mosses play a crucial role in the tundra by providing food and shelter for a variety of animals, including insects, small mammals, and birds. They also help retain moisture in the soil and prevent erosion, which is particularly important in the fragile tundra environment. Understanding “What’s a Producer in Tundra” gives insight into the resilience of these small but mighty organisms.
Arctic Grasses: Adapted to Survive the Cold
Arctic grasses are another important group of producers in the tundra. Unlike the tall grasses found in warmer climates, Arctic grasses are short, often only growing a few inches tall. These grasses are specially adapted to the short growing season and can quickly take advantage of the brief periods of warmth in the summer. They are a vital food source for herbivores like reindeer and hares, and their roots help stabilize the soil, preventing it from being blown away by the wind. This explains why “What’s a Producer in Tundra” is closely linked to the survival of these grasses.
What’s a Producer in Tundra: Producers in the Tundra Are Often Slow-Growing
One of the most fascinating facts about tundra producers is their slow growth rate. Due to the short growing season and limited availability of nutrients, many plants in the tundra grow very slowly. Some species can take years or even decades to reach maturity. For example, certain Arctic shrubs and trees may take up to 50 years to grow just a few feet tall. This slow growth rate makes the tundra’s producers particularly vulnerable to environmental changes, as it can take them many years to recover from disturbances.
The Importance of Producers in the Food Chain
Producers in the tundra are at the very bottom of the food chain. Without them, herbivores like lemmings, caribou, and Arctic hares would have no food to sustain themselves. These herbivores, in turn, provide food for predators like Arctic foxes, wolves, and birds of prey. By converting sunlight into energy, producers in the tundra provide the foundation for the entire food web. This makes them absolutely essential to the survival of many species in the region. So, when we ask, “What’s a Producer in Tundra?” the answer lies in their critical role in sustaining life.
Climate Change and its Impact on Tundra Producers
As the global climate changes, the tundra is experiencing warming temperatures, which could have a significant impact on its producers. Warmer temperatures may cause permafrost to melt, which could lead to changes in the structure of tundra vegetation. Some studies suggest that as temperatures rise, shrubs and other plants may begin to encroach upon areas once dominated by mosses and lichens. This shift in vegetation could have a ripple effect throughout the entire ecosystem, affecting herbivores and predators alike. Thus, understanding “What’s a Producer in Tundra” is becoming even more critical as climate change reshapes the landscape.
What’s a Producer in Tundra: Adaptations That Help Tundra Producers Survive
Tundra producers have developed several fascinating adaptations that help them survive in one of the harshest environments on Earth. Many plants are able to grow close to the ground, minimizing their exposure to cold winds and extreme temperatures. Others have developed special mechanisms to conserve water, such as storing it in their leaves or stems. Some producers, like Arctic willows, have flexible stems that bend in the wind rather than breaking. These adaptations help tundra producers endure the harsh conditions and continue to thrive in this extreme ecosystem, showcasing why “What’s a Producer in Tundra” is so important for survival.
Conclusion
In summary, the producers in the tundra play an essential role in maintaining the delicate balance of this extreme ecosystem. Despite the challenges posed by permafrost, short growing seasons, and freezing temperatures, plants like mosses, lichens, and Arctic grasses have adapted in incredible ways to survive. By converting sunlight into energy, these producers form the foundation of the tundra food web, providing sustenance for herbivores and, in turn, predators. As climate change threatens to alter the delicate balance of the tundra, understanding “What’s a Producer in Tundra” becomes increasingly important to ensure that this unique ecosystem continues to thrive.
FAQs
Q1. What are the main producers in the tundra?
The primary producers in the tundra are mosses, lichens, Arctic grasses, and small shrubs. These plants have adapted to survive the harsh conditions of the tundra.
Q2. How do tundra producers survive in such cold conditions?
Tundra producers have specialized adaptations such as growing close to the ground to minimize exposure to wind and cold. They also have mechanisms to conserve water and withstand low temperatures.
Q3. Why are producers so important in the tundra food chain?
Producers in the tundra are essential because they form the base of the food chain. They convert sunlight into energy, which sustains herbivores and, in turn, supports predators.
Q4. How does climate change affect tundra producers?
Climate change could cause permafrost to melt and alter the vegetation of the tundra. This could lead to shifts in plant communities, which may impact herbivores and predators that rely on them for food.
Q5. What adaptations help tundra producers survive?
Tundra producers have adaptations such as low-growing structures to avoid wind exposure, water conservation methods, and flexible stems that can bend in strong winds, helping them thrive in extreme conditions.
Also read: Its Good to Talk: The Power of Communication in Everyday Life.